Lynda Thompson on Neurofeedback and Biofeedback Synergy
- Fred Shaffer
- Sep 14, 2025
- 3 min read
Updated: Sep 15, 2025

Combine Neurofeedback and Biofeedback To Improve Outcomes
Lynda Thompson (2025) argued that multimodal interventions can be more effective in her article, "Synergy between neurofeedback and biofeedback enhances therapeutic outcome," in Applied Psychophysiology & Biofeedback.
What Was The Takeaway?

Why Combined Approaches?

What Is The History?

What Is The Neuroanatomy?

Which Metacognitive Strategies Are Valuable?

Which Multimodal Interventions Are Promising?
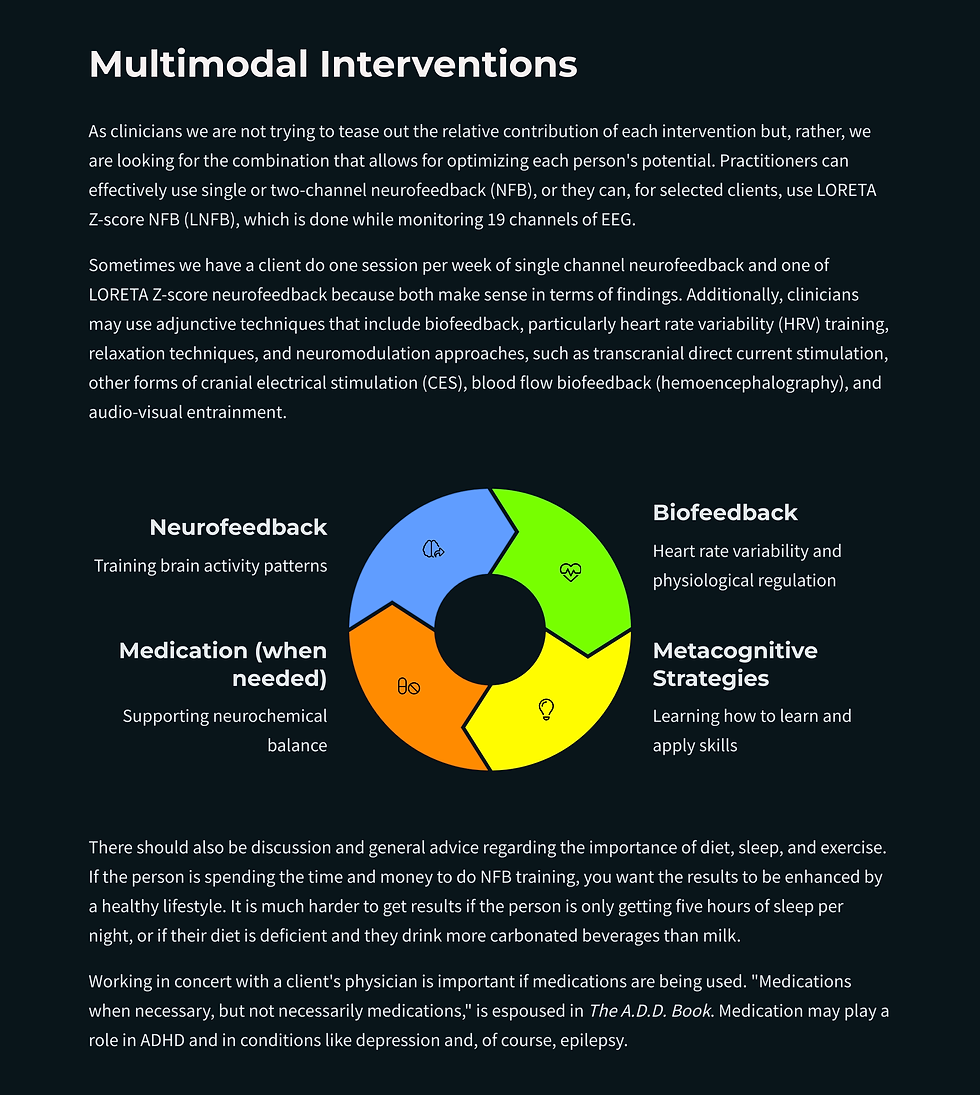
Which Newer Modalities Are Supported By Evidence?

What Are Examples of Combined Interventions?

Conclusion

Glossary
biofeedback: a technique that trains individuals to control physiological processes such as temperature, muscle tension, and respiration by providing real-time feedback from sensors.
cranial electrical stimulation (CES): a neuromodulation method using low-level electrical currents applied transcranially to influence brain activity.
desensitization: a behavioral intervention used to reduce anxiety or phobic responses through gradual exposure to the feared stimulus in a controlled manner.
diffusion tensor imaging: a neuroimaging method that maps white matter tracts in the brain by tracking the diffusion of water molecules.
electrodermal response (EDR): a measure of skin conductance reflecting sweat gland activity and sympathetic nervous system arousal.
electromyographic (EMG) artifact: unwanted electrical activity in EEG recordings caused by muscle movement.
event-related potentials (ERPs): EEG-derived waveforms reflecting the brain’s response to specific sensory, cognitive, or motor events.
galvanic skin response (GSR): an older term for electrodermal response, measuring changes in skin conductance due to emotional arousal.
heart rate variability (HRV): the variation in time intervals between heartbeats, indicating autonomic nervous system balance.
hemoencephalography: a form of biofeedback that measures changes in cerebral blood flow as an index of brain activity.
impedance: electrical resistance in EEG recording, ideally kept low to ensure high signal quality.
locus coeruleus: a brainstem nucleus involved in arousal, attention, and autonomic regulation.
LORETA Z-score neurofeedback (LNFB): a type of neurofeedback that uses low-resolution electromagnetic tomography and normative databases to guide training across multiple brain sites.
long-term potentiation (LTP): a lasting increase in synaptic strength following repeated stimulation, associated with learning and memory.
metacognitive strategies: cognitive techniques that promote awareness and control of one's learning processes, often used to enhance academic and functional performance.
neurofeedback (NFB): a type of biofeedback that provides real-time EEG-based feedback to teach self-regulation of brain activity.
nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS): a medullary structure that integrates visceral afferents from cardiovascular, respiratory, and gastrointestinal systems and modulates autonomic responses.
paraventricular nucleus: a hypothalamic structure central to the coordination of autonomic and endocrine responses to stress.
photobiomodulation (PBM): a therapy using red or near-infrared light to stimulate cellular activity, often applied for brain function enhancement.
polyvagal theory: a model proposed by Stephen Porges describing how the vagus nerve influences emotional regulation, social behavior, and physiological states.
quantitative EEG (qEEG): the numerical analysis of EEG signals to evaluate brain function, typically involving comparisons to normative databases.
sensorimotor rhythm (SMR): EEG activity in the 12–15 Hz range associated with motor inhibition and calm alertness.
spindling beta: narrow-band high-frequency EEG activity (typically 21–35 Hz) associated with hyperarousal, anxiety, or rumination.
stapedius muscle: the smallest skeletal muscle in the body, located in the middle ear, implicated in auditory processing and vagal tone regulation.
systems theory of neural synergy: a framework positing that combined interventions like neurofeedback and biofeedback produce synergistic effects via overlapping neuroanatomical pathways.
theta/beta ratio: a qEEG metric used in ADHD assessments; a higher ratio is commonly associated with inattention and underarousal.
token economy: a behavioral reinforcement system in which tokens are earned for desired behaviors and exchanged for tangible rewards.
transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS): a neuromodulatory technique that applies low electrical currents across the scalp to modulate cortical excitability.
Let me know if you’d like this expanded with acronyms, citations, or term-specific references.
Reference
Thompson, L. Synergy between neurofeedback and biofeedback enhances therapeutic outcomes. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 50, 305–314 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-025-09706-0
About the Author

Fred Shaffer earned his PhD in Psychology from Oklahoma State University. He earned BCIA certifications in Biofeedback and HRV Biofeedback. Fred is an Allen Fellow and Professor of Psychology at Truman State University, where has has taught for 50 years. He is a Biological Psychologist who consults and lectures in heart rate variability biofeedback, Physiological Psychology, and Psychopharmacology. Fred helped to edit Evidence-Based Practice in Biofeedback and Neurofeedback (3rd and 4th eds.) and helped to maintain BCIA's certification programs.
Support Our Friends









Helpful!
Great summary with helpful graphics to explain a lengthy article that delineates how to get excellent results for clients by combining interventions.. Well worth a read or listen!